Big Data Hype and Reality
Big Data V’s; the phenomenon has taken technical and the mainstream media by storm. The world seems to be awash in Big Data projects, activities, analyses, and so on.
However, as with many technology trends, there is some ambiguity in its definition, which leads to misunderstanding, vagueness, and doubt when trying to understand how it can help humanity at large.
Therefore, it is best to begin with, a definition of Big Data and Big Data V’s. Credits should go to the analyst firm Gartner for the most often used definition of Big data.
It is as follows:
“It is high-volume, high-velocity and high-variety information assets that demands cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing for enhanced insight and decision making.”
For the most of the last decade, in promoting the big data concept, the analyst community and the media have seemed to latch onto the modifications to the definition, hyperactive converging ideas on what is referred to as the “3Vs; volume, velocity, and variety”, others have built upon that buzzword to augment the definition by additional Vs such as “value” or “variability,” intended to capitalize on improvement to the definition.
In technology, over recent times, the concepts of “big data” and “big data analytics” have become ubiquitous—these are present buzzwords and whenever you visit a website, open a newspaper, or read a magazine.
Incorporation of yet many technologies into big data for tasks like massive parallelism, huge data volumes, data distribution, high-speed networks, high-performance computing, task and thread management, and data mining and analytics are not new.
Big Data and it’s perspective lenses
The term “big data” is difficult to understand because it can mean so many different things to different people. Your understanding will be different if you look at big data through a technology lens, versus a business lens or industry lens. These lenses change with what is known as V characteristics of Big data. Let us discuss, what these V’s are? and how these V’s impact the perspective and usage?
Origin of the V’s
This ubiquity of the V’s definition despite, the origin of the concept is not new, since it was analyst Dough Laney (at the time Meta Group, now Gartner) who said in a research note “3-D Data Management,” around the year 2001
“While enterprises struggle to combine systems, and collapse redundant databases to enable greater operational, analytical, and collaborative consistencies, changing economic conditions have made this job more difficult. E-commerce has exploded data management challenges along three dimensions: volumes, velocity and variety”
It was not before 2000-2002, IT organizations compiled a variety of approaches to have at their disposal for dealing with each V.
Mining the formal definition
The challenge with Gartner’s definition is twofold. First, the impact of cutting the definition to concentrate on the V’s effectively distills out two other critical components of the message:
- Profitable forms of information processing; (Achieving the benefit)
- Improved insight and decision-making; (the desired outcome)
The second is a bit understated: Implicitly, we cannot consider the statement just as a mere definition, but rather, it is as good as a brief description.
The common notion creates a confusion that: the definition is more to decide whether we are using big data solutions or even if we have problems that need a big data solution. The same issue hinders the ability to convey a value proposition because of the difficulty in scoping with the intent of the solution design, development, and delivery and what the desired result really means to us.
Addition to Big data V’s
Noticeably, Laney’s “3 Vs”, did not mention Big Data explicitly. Several authors extended the “3 Vs” model, adding other features of Big Data, such as “Veracity” by Schroeck et al in 2012, “Value” by Dijcks in the year 2013,
It is necessary to look beyond what is a marketing definition to understand the concept’s core intent as the first step in evaluating the value and veracity proposition.
Where Big Data V’s fit in?
Fundamentally, Big data is about applying advanced and cost-effective techniques for solving existing and future data-related problems where the resource requirements (for data management space, computation, or other memory needs) exceed the capabilities of classical computing environments.
Hence, with data, the V’s are growing, and this inflation continues its unstoppable march.
Starting with 2001, a decade later we had the 4 V’s of Big Data, then 5 V’s, then 7 V’s and then 10 V’s. But the most important, how these universally accepted 5 V’s have had a direct impact on data collection, monitoring, storage, analysis, and reporting is worth seeing.
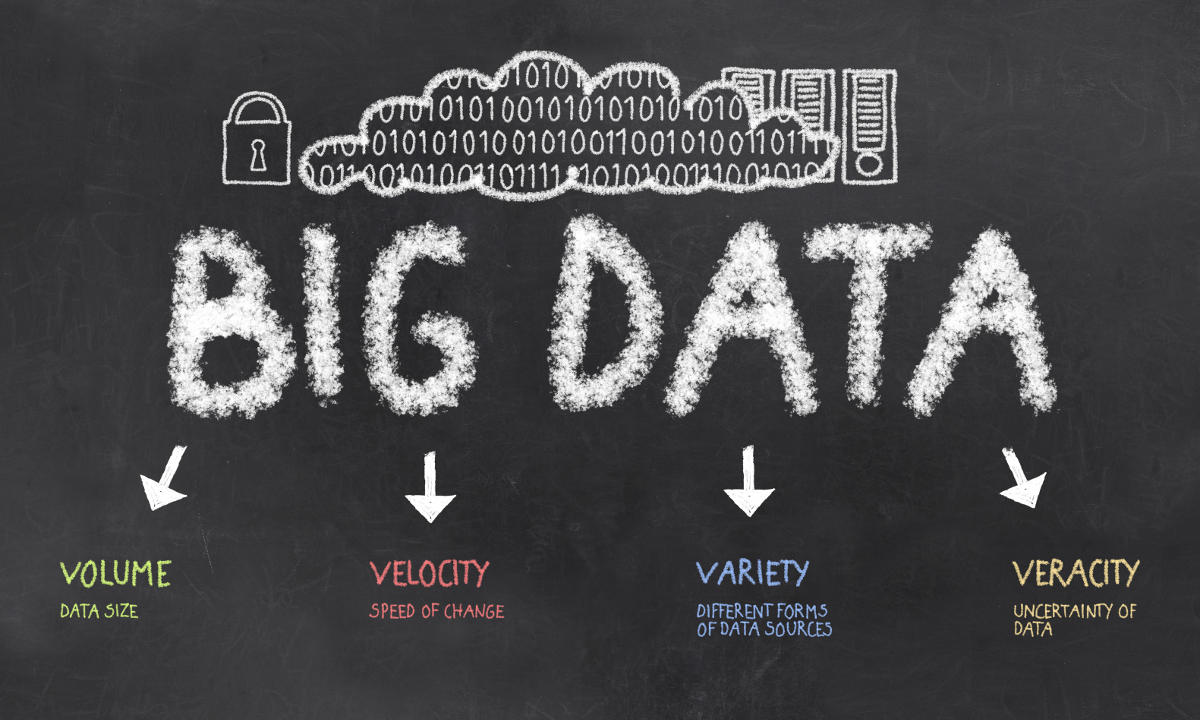
Decrypting the 5 V’s
Let us take a deep dive into the V’s of Big data, with the notion that these serve as a game-changer in current data filled the digital world. Describing Big data just using 4 V’s: Volume, Velocity, Variety, and Veracity misses out at attaching value attribute of Big data. Meanwhile, putting the fifth V into words is the Value attribute of Big data.
So, the widely accepted attributes of Big data which are universal upon are as follows:
- Volume
- Velocity
- Variety
- Veracity
- Value
Big Data V’s: The Magnitude of Big in “Big” Data?
Yes, you read it right. We are talking about the word “Big” in Big Data.
A few questions that come to our minds are as:
- What makes us say “Big”?
- Is it really that big?
- Are we exaggerating the word “Big”?
Let us find out the answer.
It is not just a word but in context to its true. Big data is really Big in volume, Big in Velocity, Big in Variety, Big in Veracity and Big in Value. The current amount of data produced is quite incredible.
Big Data V’s: The Big Statistics
Here are some examples:
- 52,459 GB of Internet traffic in 1 second
- 64,701 Google searches in 1 second
- 72,281 YouTube video videos viewed in 1 second
- 2,657,284 Emails sent in 1 second s viewed in 1 second
- 2,944 Skype calls in 1 second
You can visit http://www.internetlivestats.com/one-second/ for live statistics.
This Hugeness of Big data comes from the attributes of Big data that is the most important V’s. Let us find out what each V means to Big data.
Volume
Volume refers to the amount of data produced every second across all online channels. Volume is the best-known characteristic of big data; this is no surprise. The past few years saw the creation of more than 90 percent of all of today’s data. With data growing rapidly every day, we can no longer store and analyze data using traditional database technology.
Instead, we have seen a transitional shift to distributed systems where data storage and analysis is done in parallel. To ignore big data is no longer a choice since this data provides great insight into emerging trends, consumer preferences, and market competition. How to gather this data in real-time? .Without overwhelming existing IT infrastructures is a continual priority for us in 2018 and beyond.
Velocity
Velocity refers to the speed at which new data generated, stored, and analyzed, at any given instance of time. The figures mentioned in the earlier section “How “Big” is Big Data?” sets up the fact that the rate of data production is amazing.
Additionally, just for the sake of argument, we can undeniably say that data is continuing to increase with what is analogous to the speed of light.
With the upsurge of tablets and mobile devices, this speed is increasing beyond one’s understanding. And, as new data adds, real-time analysis of data should be our priority task. Fortunately, Big data technology today gives you the ability to instantly analyze data in the course of its generation.
Variety
Having discussed ‘3 V’s’, they certainly give us an insight into the unmentionable scale of data. The break-neck speeds at which these vast data sets grow and multiply. But only ‘Variety’ really begins to scratch the surface of the depth and significance, the challenges of Big Data.
Variety refers to the types of data that we use in our daily lives. As the technology evolves, the data does not follow a linear fashion, but it varies in size, dimension, and complexity etc. Often, categorization of this data into tables is not possible. These days around 90% of data generated is ‘unstructured’, coming in all profiles and forms from geospatial data, to visual data such as photos and videos etc.
Veracity
Veracity is the quality or reliability of the data you collect. It is important to consider the correctness and accuracy of the collected data for analysis and developing meaningful insights. In this context, when it comes to big data, preference quality over quantity. And, to focus on quality it is important to set certain metrics around the type of data collected and the data sources.
Another thing to consider is how often they need for new data arises? It can also be helpful in deciding the types of data sources to look for. So, organizing the data according to groups, value and significance will enable to draft a better strategy to use the data.
To make the right decisions, the data must be clean, consistent, and consolidated. The accuracy of the data analytics depends mostly on the veracity of the data source.
Value
Value refers to the worth of the data that is easy to access and delivers quality analytics and enables informed decisions. In fact, having endless amounts of data does not always translate into having high-value data. When trying to decode big data, it is critical to fully understand the costs and benefits of collecting and analyzing the data.
These V’s of Big data provide us the inside view of the concept. Therefore, it is not wrong to conclude that the applications of big data are limitless. Big Data is taking a lead in every sphere of our lives. The modus-operandi of business and society is already changing due to the fact we now have so much more data at our disposal. And the foremost thing is that we have the ability to analyze it.
Nevertheless, it always comes down to that fifth V: Value. How to extract value out of the data that we have?. Keeping in mind about other characteristics of Big data and their impacts too. Also, how big data can benefit humanity at large?
Conclusion
Big data with characteristics of these 5V’s delivers value in almost any area of our lives as it:
• Helps in businesses to understand and serve clients in an effective manner.
• Leverages us to optimize our business processes:
• Improves our health care by analyzing the outbreaks and track them in real-time
• Helps to improve security by ensuring to foil terrorist attacks and detect cybercrime.
• Allows sports personnel to enhance their performances using data from sensors, cameras, etc.
















Really nice piece of work .Clearly understandable .Actually I wish to make my career in big data @Nawab can you please suggest me about Bigdata.
Also notify me when you write here.
Nice one bro you should continue these things it will help u in future….
Yes. These are all the 5 v’s of big data Hadoop . But except these all ,there have another v’s of big data that are
1.Vagueness.
2.Variability.
Nice read