Pagination is the process of separating content into several discrete pages. A big e-commerce site may have several pages of content in any given category or sub-category. A visitor on this site would find it almost impossible to navigate if the webmaster chooses to display all relevant content on a single page. It can also lead to latency.
According to Google’s recommendation, search engines find it easier to crawl deep into a site with pages containing less than 100 internal or external links. Pages that go much beyond that limit stymie the efficiency of search engines to crawl the site.
Why is Pagination an SEO Issue?
-
Crawl Depth:
Just like users, the search engines prefer pages that can be reached in a few clicks. Obviously, their preference is reflected in page ranks on both Google and Bing. If you have a lot of paginated content, there is a great risk of search engines skipping over your several of your content rich pages.
-
Duplicate Content:
Generally, some pages in a same category or subcategory carry some identical content. Apart from this, pages in a series may be carrying the same Title Tag and Meta descriptions. In either case, the Google bots are averse to duplicate content and may ignore it altogether. On the other hand, it can also confuse them as to which page must be returned for a particular search query.
Duplicate content
-
Thin content:
It often happens that you may not have enough original or unique content for articles or products in the same category. Google may penalize your site for running thin content.
Pagination is essential. So, how do we optimize our paginated content for search engines?
Pagination: 5 tips for SEO
1. Pagination: Numbers of Links & Pages:
If your site has too many results, which are impossible to list on a single page, it may serve you to create categories and subcategories. For instance, a site providing information about restaurants in Mumbai. Instead of showing all 400 results on one page, you can break them up according to their location and even sub categories like vegetarian, non-vegetarian or ratings.
Extensive pagination in the case of a content rich site is not an issue as long as you have paginated your content properly. You can follow these steps to ensure that link juice flows throughout your site.
- Link to all the relevant categories & sub categories without breaking the 100 links per page limit. to keep the link juice flowing throughout the site.
- Link back to the first result page from each of the paginated URLs.
2. Pagination: Titles & Meta Descriptions
It is a common practice to run the same title and Meta description on paginated results. Especially, if the pages in the series carry products listing within the same category or sub-category. This can cause duplicate content issues and should be avoided at all costs.
- The titles tags on successive result pages in the same category can be less than optimal. This gives a clear signal to the search engines to avoid sending traffic to these pages.
- However, if the component pages in your paginated series feature unique content, you should take efforts to create unique: title tags and Meta descriptions.
- The duplicate title tags and Meta descriptions can be traced via Google Search Console in the HTML Improvements section under Search Appearance.
3. Classic Pagination for SEO: Using no index
There could be certain sections or pages on your site that you feel are relatively unimportant. It would make no difference if the search engines completely skip over these pages of content.
You can stop the search engines from indexing pages by using the no index tag. You can do this for every page in the paginated series other than the first page.
- Implement a <META NAME=”ROBOTS” CONTENT=”NOINDEX,FOLLOW”> tag within the <head> section on all pages from 2 to n.
- Including the “FOLLOW” tag in a series of pages within a category ensures that page authority travels to the individual pages throughout the list. The follow tag also helps in transferring some equity from the subsidiary pages in a series to the primary page or the site.
classic pagination
While the solution is simple and useful, it is not the preferred way of doing things as you are eliminating the chances of Google indexing your pages.
4. Most- favoured Pagination for SEO: View All Method
This is by far the most-favoured approach to pagination.
- Apart from the paginated series, you have to create a separate view all page featuring all content listed on the component pages.
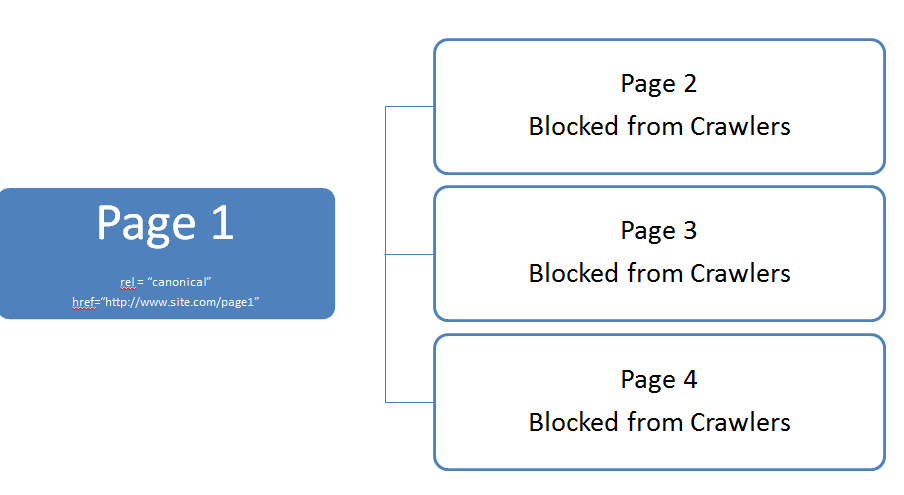
- The second step is to link back all component pages in the paginated series to the View All Page. To implement this; Place a rel=”canonical” tag within the <head> section of each paginated component page, pointing to the View-All Page.
e.g. <link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.site.com/view-all-page”/>.
While creating the view all page, ensure that it contains all content or products on the component pages. Google may not crawl all pages annotated with rel=”canonical” tag. The tag directs Google to treat each page in a paginated series as a part of the View-All page. In other words, Google will return the View-All page in related queries, instead of any of the relevant component pages of the paginated series. This approach also ensures that all component pages in a series transfer link juice to the View All directly.
However, the View-all page must load quickly to be useful. Google recommends a load time of 3 seconds at the most. Nevertheless, a survey of the top e-commerce sites reveals that anything under 4.5 seconds is acceptable. A page can also load progressively as the user scrolls down. The bottom line is that loading time should not interfere with user experience.
Several surveys stress that users prefer the view all page, provided they load seamlessly. However, this approach may not be very successful for pages with multiple images or a tremendous amount of paginated content.
5. Versatile Pagination for SEO: Use rel=”prev”/”next”
This is the most flexible approach to dealing with pagination issues. You can implement the rel=“prev” and “next” HTML attributes to indicate a series of paginated content.
By using this tag, you are creating a link between all the pages in the series. You can implement this by:
- Adding the rel=“prev” and rel=“next” to the <head> section of the page’s HTML.
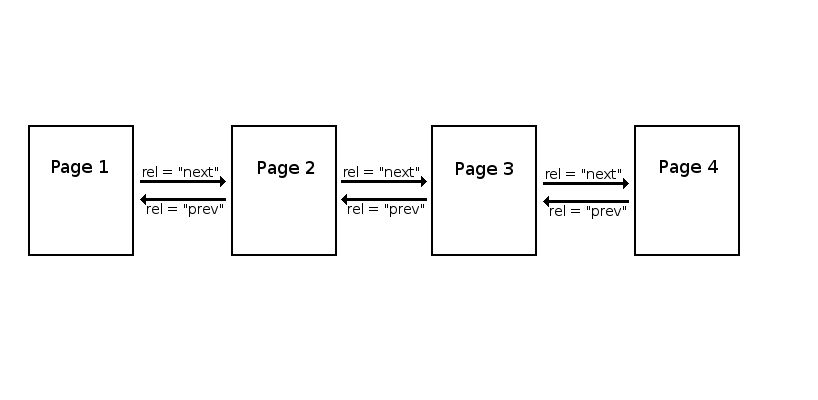
For instance, if you have 4 pages of paginated content:
Page 1: There is no page before the Page 1 in the series. So, for page 1 there is a single step.
<link rel=”next” href=”http://www.site.com/page2.html”>
Page 2: It would have both the rel=“prev” and rel=“next” to the <head> section of the page’s HTML
<link rel=”prev” href=”http://www.site.com/page1.html”>
<link rel=”next” href=”http://www.site.com/page3.html”>
Page 3:
<link rel=”prev” href=”http://www.site.com/page2.html”>
<link rel=”next” href=”http://www.site.com/page4.html”>
Page 4: The last page should only contain a rel=”prev” attribute in the <head>, as there are no further pages in the sequence:
<link rel=”prev” href=” http://www.site.com/page3.html”>
By using this sequence, you are essentially directing Google to treat all the component pages as a single entry within their index. Google will usually return the first page in response to search queries. However, there is a probability of a component page appearing in search results, if the results on that page are more relevant for a specific query.
The same link authority is passed to the first page whether you use View all page or rel=”prev”/”next”. However, there can a definite advantage to using the rel=“prev”/“next” sequence. Especially, if the component pages in the series belong to a different subcategory.
Canonicalization would direct Google to simply skip over all component pages even in instances where the component pages hold unique title tags and URLs. Whereas, if the same pages are linked together via rel=“prev”/“next”, a component page may rank for a query which is more relevant to the content on that page.
Special cases of rel=”prev”/”next”: Broken chains
Each page can be a part of only one chain at a time. In addition, paginated content must maintain an unbroken chain from the first page to the last. If you are adding a parameter to the URL’s of a paginated series, these parameters break the rel=“prev”/“next” chain. You can only link URLs with matching parameters. Once the chain is broken, the search engines will not be able to link any further pages.
Parameters are common to e-commerce sites that filter and sort content on basis of brands, prices, popularity, freshness, and the like.
a. Parameters and rel=“prev”/“next”
The rel=“prev”/“next” chain is broken every time you insert parameters in the paginated URLs. For instance, parameters that do not change the content of the page like ?referrer=parameter or unique session ID. You can work around this in two ways:
- You can direct the Googlebot not to crawl these URLs using “URL Parameters” in Webmaster Tools. However, from an SEO perspective, this is not a very good idea because it dilutes link authority that is coming into these parameterized URLs.
- The better option from an SEO perspective is to use rel=”prev”/”next” in conjunction with canonical tags.
To implement this:
- Ensure that all pages within a paginated rel=”prev”/”next” sequence are using the same parameter.
- Each URL with a parameter should link back to the non-parameterized version of the URL by using the rel=”canonical”
b. Filtered Content and rel=“prev”/“next”
You run the risk of breaking the rel=“prev”/“next” sequence when you apply parameters that filter content. Here, the content of each page depends on the filter. For example:
For example, pages that filter content on the basis of colours would have the following URLs;
Page 1: http://www.site.com/page1.html?colour=red
Page 2: http://www.site.com/page2.html?brand=red
The results on the above page will be different from;
Page 1: http://www.site.com/page1.html?colour=yellow
Page 2: http://www.site.com/page2.html?colour=yellow
To ensure that Googlebots index all the pages in a filtered category:
- You have to create separate paginated sequences for each brand filter.
- Canonical tags are not used here as the content in each series is unique.
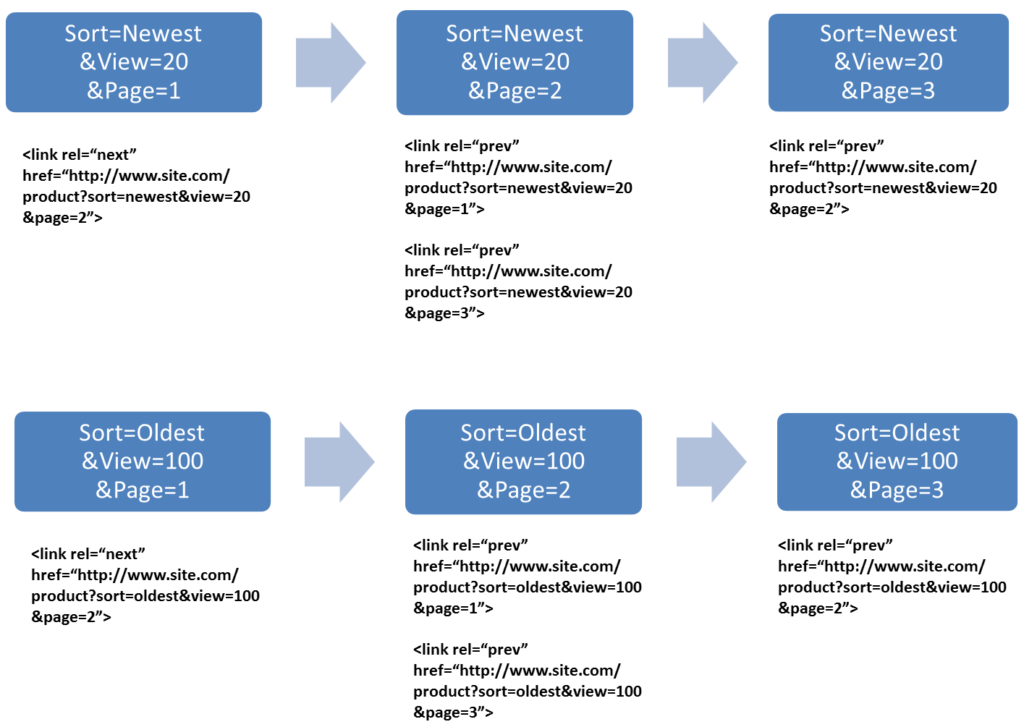
c. Sorted Content and rel=”prev”/”next”
A similar issue of URL parameters crops up with sorted content. Most e-commerce sites sort content based on price giving the user an option to view products from high to low or low to high. You also see products sorted from new to old and old to new. You have two options for sorted content:
- You can create a separate rel=”prev”/”next” sequence for the URLs of both the sorting orders. For example, a separate rel=”prev”/”next” sequence for sorting order old to new and another one for new to old. However, as the only difference between these two paginated groups is the order of the content, Google may penalize you for duplicate content.
- From SEO point of view, it is better to allow Google to index only one sorted paginated sequence. The default sort method should carry a rel=”prev”/”next” pagination method. While the other sorting method should be blocked from indexation.
-
Sorting
- This can be done by specifying the default parameter that Googlebot should crawl in the Webmaster Tool.
Advanced Pagination:
Letting Users Display More/fewer Results
Infinite scroll setups are common on e-commerce sites. This is certainly a desirable feature to improve the user experience. However, it can lead to duplicate content issues for search engines. When you create these systems, employ JavaScript/AJAX to ensure that the pages reload without creating a separate URL.
Further, ensure that the site functions properly for users who have disabled JavaScript. For this, AJAX and JavaScript navigation functions should be implemented using Progressive Enhancement.
Conclusion:
Categorising your content, unique title tags and meta descriptions should be universally employed for better rankings on search engines. The other three approaches to pagination depend on the nature of your content and requirement of your website.